Three main stages of stress
In this post, I wanted to explain why stress can be perceived differently in different situations and for different persons.
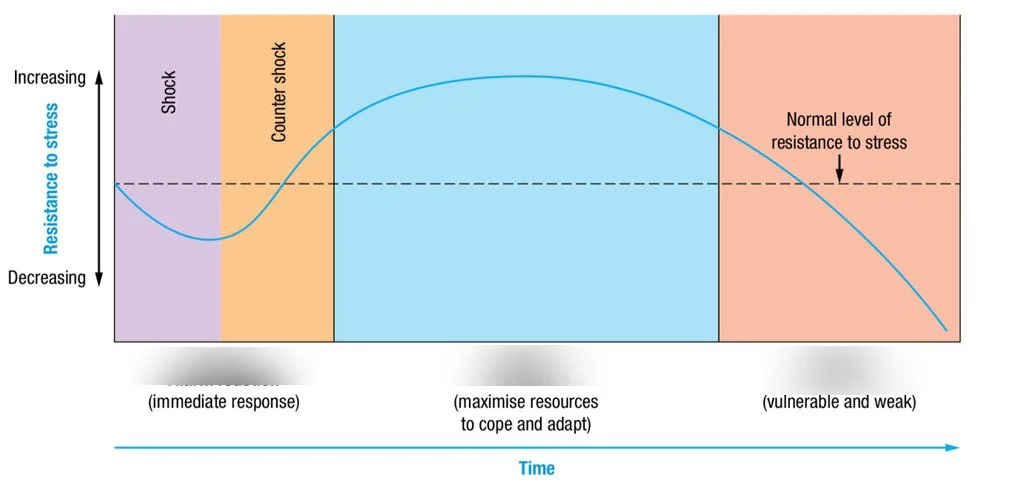
For this, I find the endocrinologist Hans Selye’s theory very enlightening. Seyle coined "general adaptation syndrome" (GAS) in 1936 to describe the responses to stress. He distinguished 3 main phases:
Alarm stage
Resistance stage
Exhaustion phase
Alarm
= the body's initial response to stress, which includes a fight-or-flight response. Generally short and intense.Resistance
= the body begins to adapt to stressors, but remains on high alert. Signs include irritability, frustration, poor concentration, sleep disturbances, and weight loss or weight gain. This phase can last several weeks, months and even years.Exhaustion
If the body remains on high alert for too long and its capacities of adaptation or its strengths get drained with insufficient replenishment, it can enter the exhaustion stage. Symptoms include chronic fatigue, depression, anxiety, weakened immune system, hormonal dysregulations and weight loss or weight gain. This phase can also last several weeks, months and years. This is where chronic conditions develop.
GAS is a term used to describe the body's response to any kind of stress, whether positive or negative. While the body can usually return to a normal state after a stressful event, spending too much time under stress can lead to serious health problems.
General Adaptation Syndrome Diagram
Possible signs & symptoms
Sleep, this is a big one and it goes in both directions; stress affects your sleep, and your sleep affects your ability to cope with stress:
you struggle to fall asleep, or to maintain sleep,
Broken sleep - you wake up multiple times
You wake up unrefreshed and fatigued, needing an hour or more to “wake-up” possibly needing several cups of coffee to go through your day.
If your sleep is poor, there are chances that your stress could be managed in a more supportive way.
Racing thoughts: you may feel overwhelmed feel you can't cope and just want it to stop and at the same time you have this negative energy that maintains you active and sometimes too active at the wrong times
Mood changes: feeling snappy or overwhelmed and unable to cope with every other responsibility coming your way
Inability to relax: you cannot relax without having to check your messages, you struggle to wind down or to take a holiday
Cognition, concentration, memory, decision-making: you feel you can't think straight anymore or your attention is elsewhere than in what you're doing, or you feel like you can't remember things as well as before
Headaches, high blood pressure: although those can have various causes, stress is a contributor, or what we call a sustaining factor.
Digestion: bloating, reflux, heartburn, loose stools or constipation